Poker Starting Hands Wiki
Find the best starting poker hands. Learn about poker starting hands and holdem starting hands. Get free tips on Texas hold em.
- Poker Starting Hands Wikipedia
- Poker Starting Hands Wiki Game
- Poker Starting Hands Wiki Fandom
- Poker Starting Hands Wiki Hands
Poker Starting Hands: How Not to Be A Fish Now that you understand the position concept we are going to expand on that by looking at the subject of which starting hands to play and which to throw in the muck. This is the area where inexperienced players become fish, simply by not having the ability to fold weak hands before the flop. How to Play Texas Holdem Starting Hands Pocket Aces. Although you can write volumes about detailed lines and theories on maximizing profit with this hand, other than folding there is rarely a scenario in which you can ever make a mistake with this hand (pre-flop that is). Poker starting hands: playing the right cards at the right time The basic idea of poker is to play the strongest poker hands in early position, good hands in mid-position and a few more hands in the late (aka strongest) position.
A poker player is drawing if they have a hand that is incomplete and needs further cards to become valuable. The hand itself is called a draw or drawing hand. For example, in seven-card stud, if four of a player's first five cards are all spades, but the hand is otherwise weak, they are drawing to a flush. In contrast, a made hand already has value and does not necessarily need to draw to win. A made starting hand with no help can lose to an inferior starting hand with a favorable draw. If an opponent has a made hand that will beat the player's draw, then the player is drawing dead; even if they make their desired hand, they will lose. Not only draws benefit from additional cards; many made hands can be improved by catching an out — and may have to in order to win.
Outs[edit]
An unseen card that would improve a drawing hand to a likely winner is an out. Playing a drawing hand has a positive expectation if the probability of catching an out is greater than the pot odds offered by the pot.
The probability of catching an out with one card to come is:
The probability of catching at least one out with two cards to come is:
| Outs | One Card % | Two Card % | One Card Odds | Two Card Odds | Draw Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2% | 4% | 46 | 23 | Backdoor Straight or Flush (Requires two cards) |
| 2 | 4% | 8% | 22 | 12 | Pocket Pair to Set |
| 3 | 7% | 13% | 14 | 7 | One Overcard |
| 4 | 9% | 17% | 10 | 5 | Inside Straight / Two Pair to Full House |
| 5 | 11% | 20% | 8 | 4 | One Pair to Two Pair or Set |
| 6 | 13% | 24% | 6.7 | 3.2 | No Pair to Pair / Two Overcards |
| 7 | 15% | 28% | 5.6 | 2.6 | Set to Full House or Quads |
| 8 | 17% | 32% | 4.7 | 2.2 | Open Straight |
| 9 | 19% | 35% | 4.1 | 1.9 | Flush |
| 10 | 22% | 38% | 3.6 | 1.6 | Inside Straight & Two Overcards |
| 11 | 24% | 42% | 3.2 | 1.4 | Open Straight & One Overcard |
| 12 | 26% | 45% | 2.8 | 1.2 | Flush & Inside Straight / Flush & One Overcard |
| 13 | 28% | 48% | 2.5 | 1.1 | |
| 14 | 30% | 51% | 2.3 | 0.95 | |
| 15 | 33% | 54% | 2.1 | 0.85 | Flush & Open Straight / Flush & Two Overcards |
| 16 | 34% | 57% | 1.9 | 0.75 | |
| 17 | 37% | 60% | 1.7 | 0.66 |
A dead out is a card that would normally be considered an out for a particular drawing hand, but should be excluded when calculating the probability of catching an out. Outs can be dead for two reasons:
- A dead out may work to improve an opponent's hand to a superior hand. For example, if Ted has a spade flush draw and Alice has an outside straight draw, any spades that complete Alice's straight are dead outs because they would also give Ted a flush.
- A dead out may have already been seen. In some game variations such as stud poker, some of the cards held by each player are seen by all players.
Types of draws[edit]
Poker Starting Hands Wikipedia
Flush draw[edit]
A flush draw, or four flush, is a hand with four cards of the same suit that may improve to a flush. For example, K♣ 9♣ 8♣ 5♣ x. A flush draw has nine outs (thirteen cards of the suit less the four already in the hand). If a player has a flush draw in Hold'em, the probability to flush the hand in the end is 34.97 percent if there are two more cards to come, and 19.56 percent (9 live cards divided by 46 unseen cards) if there is only one more card to come.
Outside straight draw[edit]
An outside straight draw, also called up and down, double-ended straight draw or open-ended straight draw, is a hand with four of the five needed cards in sequence (and could be completed on either end) that may improve to a straight. For example, x-9-8-7-6-x. An outside straight draw has eight outs (four cards to complete the top of the straight and four cards to complete the bottom of the straight). Straight draws including an ace are not outside straight draws, because the straight can only be completed on one end (has four outs).
Inside straight draw[edit]
An inside straight draw, or gutshot draw or belly buster draw, is a hand with four of the five cards needed for a straight, but missing one in the middle. For example, 9-x-7-6-5. An inside straight draw has four outs (four cards to fill the missing internal rank). Because straight draws including an ace only have four outs, they are also considered inside straight draws. For example, A-K-Q-J-x or A-2-3-4-x. The probability of catching an out for an inside straight draw is half that of catching an out for an outside straight draw.
Double inside straight draw[edit]
A double inside straight draw, or double gutshot draw or double belly buster draw can occur when either of two ranks will make a straight, but both are 'inside' draws. For example in 11-card games, 9-x-7-6-5-x-3, or 9-8-x-6-5-x-3-2, or in Texas Hold'em when holding 9-J hole cards on a 7-10-K flop. The probability of catching an out for a double inside straight draw is the same as for an outside straight draw.
Other draws[edit]
Sometimes a made hand needs to draw to a better hand. For example, if a player has two pair or three of a kind, but an opponent has a straight or flush, to win the player must draw an out to improve to a full house (or four of a kind). There are a multitude of potential situations where one hand needs to improve to beat another, but the expected value of most drawing plays can be calculated by counting outs, computing the probability of winning, and comparing the probability of winning to the pot odds.
Backdoor draw[edit]
A backdoor draw, or runner-runner draw, is a drawing hand that needs to catch two outs to win. For example, a hand with three cards of the same suit has a backdoor flush draw because it needs two more cards of the suit. The probability of catching two outs with two cards to come is:
For example, if after the flop in Texas hold 'em, a player has a backdoor flush draw (e.g., three spades), the probability of catching two outs on the turn and river is (10 ÷ 47) × (9 ÷ 46) = 4.16 percent. Backdoor draws are generally unlikely; with 43 unseen cards, it is equally likely to catch two out of seven outs as to catch one out of one. A backdoor outside straight draw (such as J-10-9) is equally likely as a backdoor flush, but any other 3-card straight combination is not worth even one out.
Drawing dead[edit]
A player is said to be drawing dead when the hand he hopes to complete will nonetheless lose to a player who already has a better one. For example, drawing to a straight or flush when the opponent already has a full house. In games with community cards, the term can also refer to a situation where no possible additional community card draws results in a win for a player. (This may be because another player has folded the cards that would complete his hand, his opponent's hand is already stronger than any hand he can possibly draw to or that the card that completes his hand also augments his opponent's.)
See also[edit]
- Poker strategy
References[edit]
- ^Odds Chart. 'How to play texas holdem poker'. Howtoplaytexasholdempoker.org. Archived from the original on 13 January 2010. Retrieved 22 February 2010.
External links[edit]
In the poker game of Texas hold 'em, a starting hand consists of two hole cards, which belong solely to the player and remain hidden from the other players. Five community cards are also dealt into play. Betting begins before any of the community cards are exposed, and continues throughout the hand. The player's 'playing hand', which will be compared against that of each competing player, is the best 5-card poker hand available from his two hole cards and the five community cards. Unless otherwise specified, here the term hand applies to the player's two hole cards, or starting hand.
Essentials[edit]
There are 1326 distinct possible combinations of two hole cards from a standard 52-card deck in hold 'em, but since suits have no relative value in this poker variant, many of these hands are identical in value before the flop. For example, A♥J♥ and A♠J♠ are identical in value, because each is a hand consisting of an ace and a jack of the same suit.
Poker Starting Hands Wiki Game
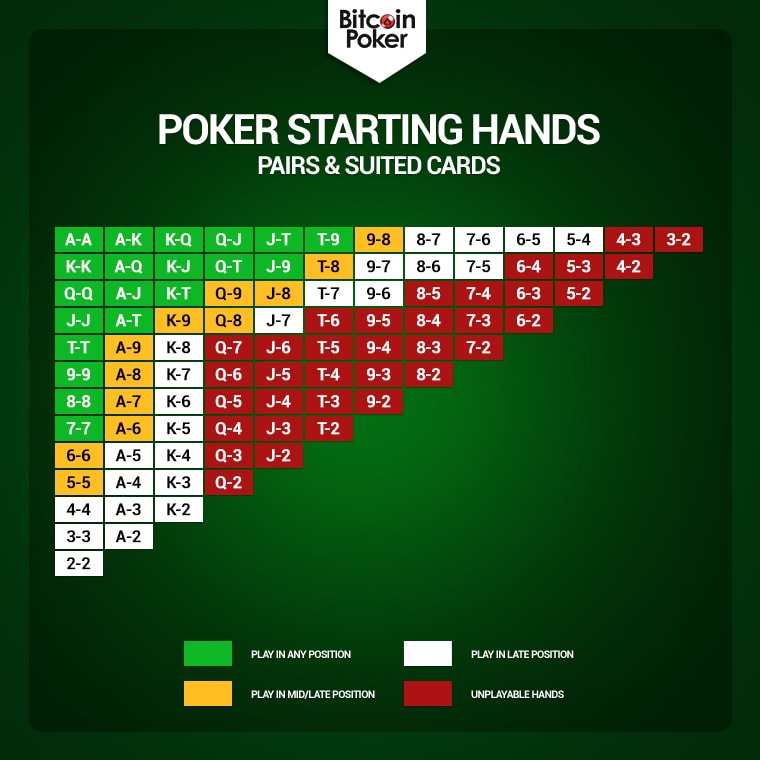
Therefore, there are 169 non-equivalent starting hands in hold 'em, which is the sum total of : 13 pocket pairs, 13 × 12 / 2 = 78 suited hands and 78 unsuited hands (13 + 78 + 78 = 169).
These 169 hands are not equally likely. Hold 'em hands are sometimes classified as having one of three 'shapes':
- Pairs, (or 'pocket pairs'), which consist of two cards of the same rank (e.g. 9♠9♣). One hand in 17 will be a pair, each occurring with individual probability 1/221 (P(pair) = 3/51 = 1/17).
- Alternative means of making this calculation
- First Step
- As confirmed above.
- There are 1326 possible combination of opening hand.
- Second Step
- There are 6 different combos of each pair. 9h9c, 9h9s, 9h9d, 9c9s, 9c9d, 9d9s. Therefore, there are 78 possible combinations of pocket pairs (6 multiplied by 13 i.e. 22-AA)
- To calculate the odds of being dealt a pair
- 78 (the number of any particular pair being dealt. As above) divided by 1326 (possible opening hands)

- 78/1326 = 0.058 or 5.8%
- Suited hands, which contain two cards of the same suit (e.g. A♣6♣). 23.5% of all starting hands are suited.

Poker Starting Hands Wiki Fandom
Probability of first card is 1.0 (any of the 52 cards)Probability of second hand suit matching the first:There are 13 cards per suit, and one is in your hand leaving 12 remaining of the 51 cards remaining in the deck. 12/51=.2353 or 23.5%
- Offsuit hands, which contain two cards of a different suit and rank (e.g. K♠J♥). 70.6% of all hands are offsuit hands
Offsuit pairs = 78Other offsuit hands = 936
It is typical to abbreviate suited hands in hold 'em by affixing an 's' to the hand, as well as to abbreviate non-suited hands with an 'o' (for offsuit). That is,
Poker Starting Hands Wiki Hands
- QQ represents any pair of queens,
- KQ represents any king and queen,
- AKo represents any ace and king of different suits, and
- JTs represents any jack and ten of the same suit.
Limit hand rankings[edit]
Some notable theorists and players have created systems to rank the value of starting hands in limit Texas hold'em. These rankings do not apply to no limit play.
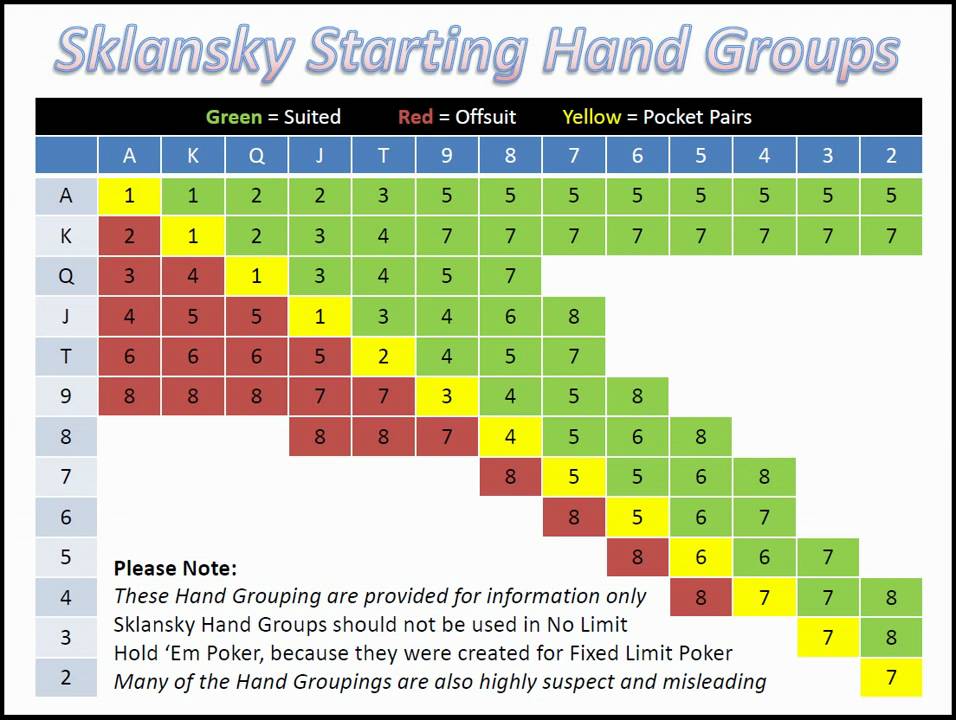
Sklansky hand groups[edit]
David Sklansky and Mason Malmuth[1] assigned in 1999 each hand to a group, and proposed all hands in the group could normally be played similarly. Stronger starting hands are identified by a lower number. Hands without a number are the weakest starting hands. As a general rule, books on Texas hold'em present hand strengths starting with the assumption of a nine or ten person table. The table below illustrates the concept:
Chen formula[edit]
The 'Chen Formula' is a way to compute the 'power ratings' of starting hands that was originally developed by Bill Chen.[2]
- Highest Card
- Based on the highest card, assign points as follows:
- Ace = 10 points, K = 8 points, Q = 7 points, J = 6 points.
- 10 through 2, half of face value (10 = 5 points, 9 = 4.5 points, etc.)
- Pairs
- For pairs, multiply the points by 2 (AA=20, KK=16, etc.), with a minimum of 5 points for any pair. 55 is given an extra point (i.e., 6).
- Suited
- Add 2 points for suited cards.
- Closeness
- Subtract 1 point for 1 gappers (AQ, J9)
- 2 points for 2 gappers (J8, AJ).
- 4 points for 3 gappers (J7, 73).
- 5 points for larger gappers, including A2 A3 A4
- Add an extra point if connected or 1-gap and your highest card is lower than Q (since you then can make all higher straights)
Phil Hellmuth's: 'Play Poker Like the Pros'[edit]
Phil Hellmuth's 'Play Poker Like the Pros' book published in 2003.
| Tier | Hands | Category |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | AA, KK, AKs, QQ, AK | Top 12 Hands |
| 2 | JJ, TT, 99 | |
| 3 | 88, 77, AQs, AQ | |
| 4 | 66, 55, 44, 33, 22, AJs, ATs, A9s, A8s | Majority Play Hands |
| 5 | A7s, A6s, A5s, A4s, A3s, A2s, KQs, KQ | |
| 6 | QJs, JTs, T9s, 98s, 87s, 76s, 65s | Suited Connectors |
Statistics based on real online play[edit]
Statistics based on real play with their associated actual value in real bets.[3]
| Tier | Hands | Expected Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | AA, KK, QQ, JJ, AKs | 2.32 - 0.78 |
| 2 | AQs, TT, AK, AJs, KQs, 99 | 0.59 - 0.38 |
| 3 | ATs, AQ, KJs, 88, KTs, QJs | 0.32 - 0.20 |
| 4 | A9s, AJ, QTs, KQ, 77, JTs | 0.19 - 0.15 |
| 5 | A8s, K9s, AT, A5s, A7s | 0.10 - 0.08 |
| 6 | KJ, 66, T9s, A4s, Q9s | 0.08 - 0.05 |
| 7 | J9s, QJ, A6s, 55, A3s, K8s, KT | 0.04 - 0.01 |
| 8 | 98s, T8s, K7s, A2s | 0.00 |
| 9 | 87s, QT, Q8s, 44, A9, J8s, 76s, JT | (-) 0.02 - 0.03 |
Nicknames for starting hands[edit]
In poker communities, it is common for hole cards to be given nicknames. While most combinations have a nickname, stronger handed nicknames are generally more recognized, the most notable probably being the 'Big Slick' - Ace and King of the same suit, although an Ace-King of any suit combination is less occasionally referred to as an Anna Kournikova, derived from the initials AK and because it 'looks really good but rarely wins.'[4][5] Hands can be named according to their shapes (e.g., paired aces look like 'rockets', paired jacks look like 'fish hooks'); a historic event (e.g., A's and 8's - dead man's hand, representing the hand held by Wild Bill Hickok when he was fatally shot in the back by Jack McCall in 1876); many other reasons like animal names, alliteration and rhyming are also used in nicknames.
Notes[edit]
- ^David Sklansky and Mason Malmuth (1999). Hold 'em Poker for Advanced Players. Two Plus Two Publications. ISBN1-880685-22-1
- ^Hold'em Excellence: From Beginner to Winner by Lou Krieger, Chapter 5, pages 39 - 43, Second Edition
- ^http://www.pokerroom.com/poker/poker-school/ev-stats/total-stats-by-card/[dead link]
- ^Aspden, Peter (2007-05-19). 'FT Weekend Magazine - Non-fiction: Stakes and chips Las Vegas and the internet have helped poker become the biggest game in town'. Financial Times. Retrieved 2010-01-10.
- ^Martain, Tim (2007-07-15). 'A little luck helps out'. Sunday Tasmanian. Retrieved 2010-01-10.